Acoustics included as part of a major education research project

Amanda Robinson has been a key researcher gathering acoustic metrics for innovative learning environments and she presented the findings at EIAS2023 this year. Traditional acoustic parameters are often used to describe the environment within learning environments. These include metrics such as ambient sound levels, reverberation time and sound reduction to adjoining spaces. For this recent study, additional acoustic parameters beyond the traditional ones have been used to evaluate these types of environments. These included; speech intelligibility, privacy distance, and spatial decay distance in a range of different types of education spaces. The spaces varied in terms of floor area, volume and whether the space was partitioned from the surrounding area.
Amanda’s presentation explored the strengths and limitations of the acoustic metrics. Analysed whether there are additional insights that can be used to assist speakers and listeners in innovative learning environments.
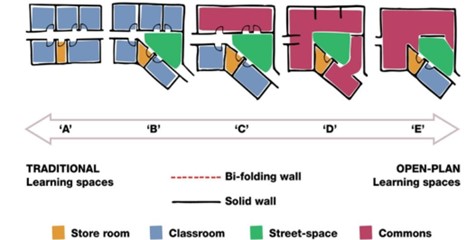
Learning space typologies in the context of the different types of existing schools

One of the first steps was identifying which spaces provided the optimal learning environment (on all fronts). How do the acoustics of type A/B spaces compare with type D/E learning spaces? These type of spaces respond to the ways in which we are encouraging students to learn, which is much more interactive and collaborative.
Based on the Australian 21st century school blueprint
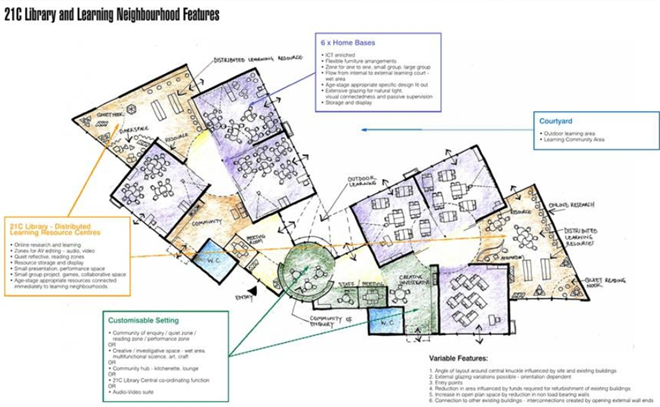
The above school plan is a typical design implemented Australia wide.
Acoustics was monitored as it’s importance was recognised as a aspect for effective learning environments
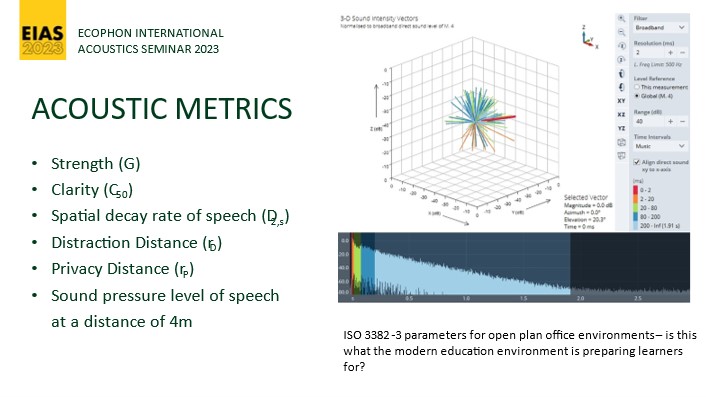
The Acoustic Metrics overview and their target levels:
- Sound strength/ room gain – G = measure of contribution of reflected sound to the direct sound from a sound source – G>15 for primary classrooms
- Speech clarity – C50 = ratio of early to late energy arriving. Direct and early reflections before 50ms = good, late energy = reverberant field. Higher C = more clarity, and 3 has been suggested for primary aged children
- D2,s = rate of decay per doubling of distance – poor offices is where D2s is less than 5, but good acoustics is greater than 7
- Distraction distance = where speech transmission falls below 0.5
- Privacy distance = where speech transmission falls below 0.2
Watch Amanda’s EIAS2023 presentation here.
More about EIAS here
More about the ILETC Innovative Learning environments research spatial typologies here.


